
Managing corporate treasury operations with traditional wallets can be risky and inefficient. Multi-Party Computation (MPC) wallets solve these issues by splitting private keys into multiple shares, enhancing security and flexibility. These wallets allow for distributed control, reducing risks like fraud or loss due to a single point of failure. They also streamline workflows, lower transaction fees, and work across blockchains.
Key Takeaways:
What are MPC Wallets? Cryptographic wallets that split private keys into shares, ensuring no single entity has full control.
Why use them? They reduce security risks, allow flexible governance, and simplify treasury management.
How to set up? Define your organization's needs, configure access controls, enforce transaction policies, and ensure compliance.
MPC wallets are ideal for businesses handling stablecoins, multi-chain transactions, and regulatory requirements. This guide explains how to implement them step-by-step for secure and efficient treasury operations.
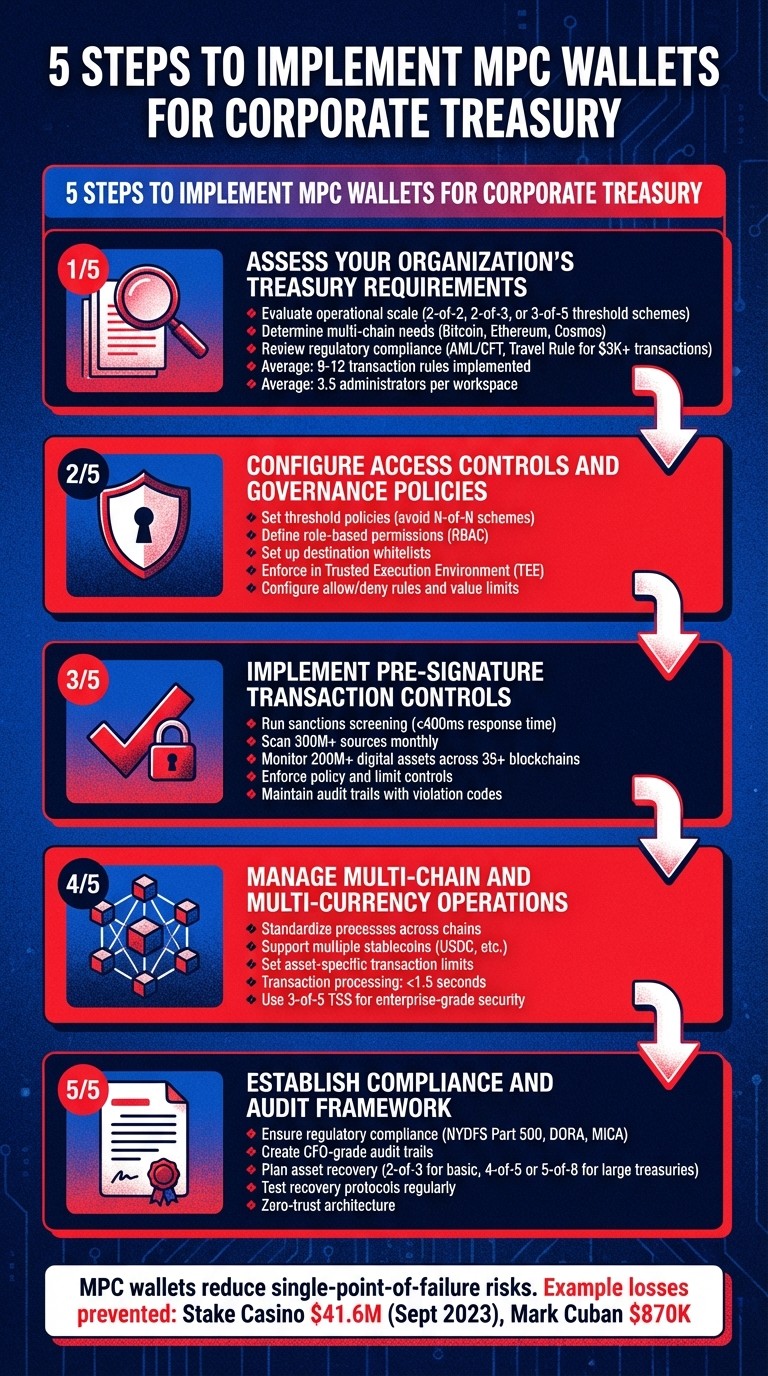
5-Step Process for Setting Up MPC Wallets for Corporate Treasury
Securing crypto with Multi-Party Computation (MPC)
Step 1: Assess Your Organization's Treasury Requirements
Before diving into implementing an MPC wallet, it's crucial to understand your treasury's specific needs. A startup paying 20 vendors monthly will have vastly different requirements compared to a trading desk handling hundreds of transactions daily. Here's how you can tailor your MPC wallet setup to fit your treasury's scale, blockchain needs, and compliance environment.
Evaluate Operational Scale and Complexity
Start by assessing your team structure and how often transactions occur. This will help you choose the right threshold scheme - essentially, the number of approvals needed to authorize a transaction. For most basic setups, a 2-of-2 scheme offers a good balance between security and speed. However, if you're managing larger assets, consider a 2-of-3 setup for added redundancy, or even a 3-of-5 configuration for enterprise-level protection.
Transaction volume is another key factor. High-frequency trading might experience delays with certain MPC protocols, while standard payroll and vendor payments typically run without a hitch. Think about your specific workflows. For example, does your marketing team require separate spending limits? Should weekend transfers over $10,000 need additional approvals? These details can help you decide if you need features like time-locking, multi-step approvals, or whitelisted addresses for frequently used protocols.
Your setup should also account for device failures. As Krayon points out:
At bare minimum a two of three approval process should be sufficient... if you're managing a sizeable treasury you should consider implementing a much bigger quorum, perhaps 4 of 5 or 5 of 8.
Make sure your threshold rules align with governance policies to minimize risks across all treasury activities.
Determine Multi-Chain and Stablecoin Requirements
Once you've nailed down your internal needs, it's time to look at external dependencies like blockchain compatibility and stablecoin options. MPC wallets work seamlessly across networks like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Cosmos using uniform cryptographic protocols.
For tasks like payroll and vendor payments, using native stablecoins on Layer-2 networks can reduce costs and speed up transactions. If your team interacts with DeFi protocols or Web3 applications, consider whitelisting relevant contract addresses. This allows your team to operate independently without requiring quorum approval for every transaction. Additionally, implement automated safeguards - such as halting operations if a stablecoin loses its peg or a cross-chain bridge fails - to avoid costly errors during market fluctuations.
Review Regulatory and Compliance Requirements
Regulatory compliance is non-negotiable. For instance, the GENIUS Act, signed into law on July 18, 2025, classifies stablecoin issuers and related entities as financial institutions under the Bank Secrecy Act. This means full AML/CFT obligations now apply. Your treasury setup must support sanctions screening, Travel Rule compliance for transactions over $3,000, and fiduciary accountability through separation of duties.
MPC wallets can enhance privacy by recording only a single signature on the blockchain, keeping your internal approval structure confidential. However, you still need robust audit trails. On average, institutional MPC users implement 9 to 12 transaction rules to ensure security and compliance. For example, Fireblocks users typically have 3.5 administrators per workspace to maintain quorum for critical changes. Establish a maker/checker workflow where no single person can both initiate and approve a transaction. Use destination whitelisting to restrict outgoing transfers to vetted counterparties.
Step 2: Configure Access Controls and Governance Policies
Once you've mapped out your treasury requirements, the next step is to establish a governance framework. This framework defines who can perform specific actions and under what conditions. Essentially, you're translating your organization's approval workflows into machine-enforceable rules. The goal? To eliminate single points of failure while ensuring daily treasury operations remain efficient.
Set Threshold Policies and Signing Requirements
Threshold signature schemes (TSS) determine how many approvals are needed before a transaction can proceed. Common setups include:
2-of-2: Used for standard operations.
2-of-3: Adds redundancy in case a key is lost.
3-of-5: Provides enterprise-level oversight and flexibility.
"The M-of-N threshold should be chosen to balance security and operational resilience. Avoid N-of-N schemes, as the loss of a single key would result in a permanent loss of access to all funds." - SEAL Security Frameworks
It's critical to avoid N-of-N schemes, where every signer must approve. Losing just one key in this setup could permanently lock access to funds. Instead, build redundancy into your system to ensure continuity.
Define Role-Based Permissions and Approval Workflows
Role-based access control (RBAC) allows you to assign permissions based on team roles. For instance, routine payments might be handled by specific team members, while transactions above a certain threshold would require approval from higher-level executives, such as the CFO. Modern MPC platforms make this easier by supporting hierarchical governance structures. You can define rules across different levels, such as:
Workspace level: Company-wide policies.
Portfolio level: Rules grouped by risk or asset type.
Individual wallet level: Granular controls for specific wallets.
To ensure these policies are enforced without exceptions, they should run in a Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) before any transaction is signed. This ensures that rules cannot be bypassed at the client level. You can configure various rule types, including:
Allow/deny rules: Restrict transactions to specific contract addresses or networks.
Value limits: Set maximum transfer amounts per transaction for tokens like USDC.
Address evaluations: Inspect the full execution path, including proxy contracts, to block unauthorized interactions.
For enhanced security, consider an "allowlist-only" mode. In this setup, all transactions are blocked by default unless the destination address is explicitly approved.
Set Up Destination Whitelists and Time-Based Rules
Whitelisting trusted addresses ensures funds are sent only to vetted recipients, such as regular vendors or payroll providers. When dealing with tokens like USDC on Ethereum, make sure to whitelist both proxy and current implementation addresses.
Time-based rules add an extra layer of security. For example, you could require additional approvals for weekend transfers exceeding a specific limit or enforce a mandatory delay (timelock) between approval and execution for high-value transactions.
"Rules apply at signing time, not just after execution. This means developers can trust that no transaction leaves the wallet unless it passes policy checks." - Dynamic
To monitor compliance, set up policy violation webhooks (e.g., waas.policy.violation). These alerts notify you whenever a transaction is blocked, helping you quickly debug flagged transactions and identify potential threats before they escalate. Always test new policy rules on a testnet to ensure compliant transactions proceed smoothly and violations are correctly flagged.
Step 3: Implement Pre-Signature Transaction Controls
Once your governance policies are set up, the next vital step is pre-signature verification. This process ensures every transaction is validated before it’s cryptographically signed, not after. The aim? To eliminate "blind signing." Each participant in your MPC quorum must independently confirm that a transaction aligns with organizational policies before contributing their key share. These pre-signature controls build on your existing governance framework, adding another layer of security to transaction execution.
"Policies are enforced before a transaction is signed ensuring there is validation before execution." - Dynamic
This layer ensures that every transaction undergoes thorough validation before signing. Even transactions that have already been approved won’t proceed unless they pass automated compliance checks. Adopting a "zero-trust" approach means no single party or system is automatically trusted - every action must be verified against your policy engine. These measures strengthen your defenses, ensuring that no transaction bypasses scrutiny.
Run Sanctions Screening and Risk Assessments
Before any payment leaves your wallet, real-time address screening is essential to identify risks such as sanctions violations, scams, or mixing services. Blockchain intelligence platforms can provide a complete risk assessment in under 400 milliseconds. These tools scan over 300 million sources monthly, including the dark web and official sanctions lists, to link crypto wallets to real-world entities.
It’s critical to evaluate every address involved in a transaction - not just the destination. This includes intermediate contracts and proxies. Risk engines offer over 150 customizable configurations, enabling you to set thresholds for ownership risk, counterparty exposure, and indirect exposure. These engines also monitor over 200 million digital assets across 35+ blockchains, including ERC-20 tokens and stablecoins.
Set up policy violation webhooks (e.g., waas.policy.violation) to receive instant alerts when a transaction is blocked. These alerts provide detailed information about why the transaction failed - whether it’s due to a denied address, an exceeded value limit, or a flagged security risk. This real-time monitoring not only helps identify potential threats but also allows you to debug legitimate transactions that were incorrectly flagged.
Enforce Policy and Limit Controls
Your MPC wallet should enforce transaction policies during the signing process using transaction simulation. This step runs the transaction against your established rules to detect non-compliant requests or potential failures. Any transaction that doesn’t meet the criteria is automatically rejected, without requiring manual intervention. This enforcement extends the governance framework from Step 2, creating a seamless control system.
"Integrating policy enforcement within the MPC quorum - where each participant validates policy rules before computing their share - is emerging as a preferred zero-trust pattern." - Cordial Systems
Set granular value limits for both native tokens (e.g., ETH, SOL) and custom tokens (e.g., USDC). For instance, you could restrict USDC transfers to $50,000 per transaction and $200,000 per day. For heightened security, enable allowlist-only mode, where all addresses are blocked by default unless explicitly approved. This "deny-by-default" approach serves as a strong barrier against unauthorized transactions.
Running your system in a TEE (Trusted Execution Environment) ensures that client-level circumvention isn’t possible. Additionally, tagging payments with purpose codes - such as "payroll", "vendor", or "refund" - creates human-readable receipts that can be directly integrated into your corporate ledger.
With these enforcement measures in place, maintaining detailed logs becomes a critical step.
Maintain Audit Trails and Compliance Reporting
Every policy update, transaction attempt, and violation must be logged to create detailed audit records that comply with regulatory and fiduciary standards. These logs should capture every session detail, quorum participant, policy evaluated, and the final transaction hash. Such meticulous record-keeping is necessary to meet regulations like NYDFS Part 500, DORA, and MiCA.
Categorize violations with specific reason codes to streamline forensic analysis. Common codes include address_denied (blocked due to deny list or missing allowlist entry), value_limit_exceeded (transaction exceeds maximum limits), and security_risk_malicious (flagged as potentially malicious by security validation). Each violation should include key data such as denied addresses, asset types, attempted values, and validation outcomes.
Conduct monthly control attestations and recovery drills to ensure your policies remain effective and your team is prepared to handle incidents. Implement automated halt rules to pause transaction flows under specific risk conditions, such as a stablecoin de-pegging or a bridge being paused. These proactive measures help maintain business continuity while adhering to strict compliance requirements.
Step 4: Manage Multi-Chain and Multi-Currency Operations
Once your pre-signature controls are set, the next step is to streamline treasury management across multiple blockchains and currencies. With MPC wallets, you can handle operations across various blockchain networks and stablecoins without needing separate wallet systems. Since MPC wallets operate at the cryptographic layer rather than the protocol layer, a single signing engine can support Bitcoin, Ethereum, Solana, and Cosmos seamlessly.
Standardize Processes Across Chains
MPC wallets stand out because they don’t require protocol-specific implementations like multisig wallets. Instead, a unified signing engine ensures the same governance rules apply across all blockchains. This means your policies - such as destination allowlists, transaction value limits, and quorum thresholds - remain consistent whether you're transferring USDC on Ethereum or SOL on Solana. These rules align with the RBAC policies defined earlier.
Advanced MPC setups take this a step further by separating access control from key storage. This allows for dynamic updates to permissions, which is particularly useful as treasury teams grow or restructure. For example, you can adjust your quorum from 2-of-3 to 3-of-5 without needing to change the wallet's public address or transfer funds.
Once these standardized processes are in place, you can extend them to manage a variety of asset types effectively.
Support Multi-Currency Treasury Management
Handling multiple stablecoins introduces unique challenges, such as ensuring assets are sent to the correct contracts or avoiding malicious proxies. To address this, configure your MPC wallet to recognize only verified proxy and implementation addresses for each stablecoin. For instance, USDC's official contracts on Ethereum, Polygon, and Base should be pre-verified.
Additionally, set asset-specific transaction limits to mitigate risk. For example, you could allow transactions up to $100,000 for USDC but restrict volatile native tokens to $10,000 per transaction. These granular controls help safeguard your treasury while maintaining flexibility.
Build Scalable Infrastructure for Growth
As your treasury operations grow, scalability becomes critical. A robust MPC infrastructure uses distributed node clusters across global regions to ensure low-latency transaction processing - typically under 1.5 seconds. An orchestration layer can dynamically balance transaction loads across regions, making it easier to handle increasing volumes.
For resilience, implement fault tolerance with a t-of-n quorum distributed across diverse infrastructure types, such as bare-metal servers, secure enclaves, and multi-cloud environments. This ensures continuity even if specific nodes or regions experience failures.
For enterprise-grade security, consider a 3-of-5 threshold signature scheme (TSS). This approach distributes key shares across various platforms, including servers, user devices, cloud storage, and enterprise APIs. By doing so, you eliminate single points of failure while maintaining strong oversight and control.
Step 5: Establish a Compliance and Audit Framework
The final step in securing your treasury is setting up a compliance framework that aligns with auditor and regulatory requirements. With MPC wallets, key security is separated from authorization controls, allowing for features like withdrawal limits and whitelist enforcement without altering the underlying key material.
Ensure Regulatory Compliance
MPC wallets are designed to help organizations meet regulatory standards such as NYDFS Part 500, DORA, and MiCA. A zero-trust architecture plays a central role here - every action is verified, and policy enforcement is embedded directly into the signing quorum. To kick things off, consider forming a Digital Asset Steering Committee that includes executive leadership, along with representatives from technology, cybersecurity, and compliance teams. On average, enterprise MPC platforms assign about 3.5 administrators per workspace to maintain effective oversight.
For compliance at the transaction level, implement a rule engine for pre-signature policy enforcement. This system can automatically approve, block, or flag transactions for extra approvals based on factors like size, volume, or destination. Many organizations set up around nine transaction rules, with some opting for more robust setups that include 12 or more rules. Destination whitelisting is another common practice, restricting transfers to pre-approved addresses.
To strengthen these compliance measures, focus on creating transparent and detailed audit trails that meet CFO-grade standards.
Create CFO-Grade Evidence for Audit Trails
When it comes to audit trails, the goal is to achieve a level of transparency and traceability that satisfies even the most stringent CFO requirements. MPC systems provide detailed logs that capture critical information, such as who initiated the signing session, which quorum members participated, what policies were evaluated, and the final transaction hashes. Advanced systems can even cryptographically bind digital signatures to session metadata, ensuring accountability and adherence to policies for every transaction.
"From a security auditing perspective, MPC systems must emit detailed logs at each step: Who initiated the signing session? Which quorum members participated? What policy was evaluated and by whom? What transaction hash was ultimately signed?" – Cordial Systems
To ensure thorough oversight, configure your system to automatically log every policy update, transaction stage, and policy violation. Real-time monitoring tools, such as webhooks, can send instant notifications for every on-chain transaction or policy breach, providing a comprehensive audit trail that aligns with governance standards.
Pair these logs with strong recovery protocols to maintain operational continuity.
Plan for Asset Recovery and Business Continuity
In addition to pre-signature controls, establish reliable asset recovery procedures. Unlike traditional methods that rely on seed phrases, MPC recovery involves reinitializing quorum participants using backed-up key shares, reducing the risk of a single point of failure. For basic operations, a 2-of-3 threshold signature scheme works well, while larger treasuries might benefit from setups like 4-of-5 or 5-of-8.
To maximize resilience, distribute encrypted key shares across diverse infrastructures, such as secure enclaves and third-party custodians. Key generation ceremonies can further enhance security by ensuring no single individual has access to all key shares.
"Fireblocks ensures that customers can recover from the loss of access to their keys or in the event of Fireblocks service disruptions." – Michael Shaulov, Co-founder & CEO, Fireblocks
Regularly test your recovery protocols and document them thoroughly so that authorized personnel can execute them under pressure. This level of preparation ensures that treasury operations remain uninterrupted, even if specific nodes, regions, or team members are unavailable.
Conclusion: Build a Secure and Scalable Treasury System with MPC Wallets
Using MPC wallets for corporate treasury operations addresses critical vulnerabilities, significantly reducing the risks tied to single points of failure. For example, in September 2023, the Australian crypto casino Stake suffered a $41.6 million loss due to a leaked key, and billionaire Mark Cuban lost $870,000 from a compromised hot wallet. By dividing key control among multiple parties, MPC technology offers a robust solution to such threats.
This guide outlines five essential steps to establish a zero-trust architecture with built-in policy enforcement. Unlike multi-signature wallets that are tied to specific protocols and expose signers on-chain, MPC operates at the cryptographic layer. This allows a single signing engine to support multiple blockchains without requiring the redeployment of smart contracts. The result? A secure framework that not only protects assets but also simplifies operations across various blockchains.
As Cordial Systems highlights:
"MPC wallets represent one of the most important evolutions in the secure custody of digital assets." – Cordial Systems
MPC's chain-agnostic design, discussed earlier, brings unmatched flexibility to treasury management. Organizations can update signing quorums or rotate participants without altering the wallet's public address, avoiding the hassle of asset migrations. This unified approach to asset management spans Bitcoin, Ethereum, Solana, and more. With 56% of financial institutions prioritizing wallet infrastructure for stablecoin flows, MPC delivers the security and scalability essential for modern treasury operations.
To get started, consider implementing a 2-of-2 threshold, destination whitelists, and separating key security from authorization policies. This setup supports diverse use cases, from stablecoin payroll to automated vendor payments, all while maintaining the compliance and audit trails that CFOs and regulators demand.
FAQs
What advantages do MPC wallets offer for corporate treasury operations compared to traditional wallets?
MPC (Multi-Party Computation) wallets step up security by replacing the traditional single private key with threshold signatures. This means multiple parties must approve transactions, making it far harder for unauthorized access or key breaches to occur.
These wallets also offer precise control over treasury management. Teams can set up custom policies, implement maker-checker workflows, and share responsibilities, all while staying aligned with internal governance rules. On top of that, MPC wallets work seamlessly across different blockchains, providing the flexibility needed to handle stablecoin and blockchain-based financial transactions with both efficiency and security.
How do MPC wallets improve security and ensure compliance for corporate treasury operations?
MPC wallets take security to the next level by dividing a private key into several parts, or "shares", so no single entity ever holds the complete key. This distributed method significantly lowers the chances of unauthorized access or key breaches.
On the compliance side, MPC wallets empower corporate treasuries to implement policy-driven controls across various blockchains and currencies. They enable shared responsibility, reduce operational risks, and ensure strict adherence to governance protocols. This makes them a perfect fit for managing assets in intricate, multi-chain ecosystems.
What are the steps to set up an MPC wallet for corporate treasury operations?
Setting up an MPC (Multi-Party Computation) wallet for corporate treasury operations requires careful planning to ensure security, compliance, and smooth functionality. Here’s how to get started:
Begin by defining the roles and transaction approval thresholds. For example, decide how many parties must approve a transaction, such as a 2-of-3 setup. This approach balances security with operational control, ensuring no single party has complete authority.
Next, generate and distribute key shares among the designated participants. Each party should securely exchange their public and private shares, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected during the process. Once the keys are in place, establish a dedicated workspace or vault to manage the wallets efficiently.
Configure important policies like transaction limits, approval workflows, and allow-listed addresses to match your company’s governance requirements. These safeguards help prevent unauthorized activities and align wallet operations with your internal protocols.
Finally, integrate the wallet into your treasury system using API credentials. Test its functionality by simulating real-world transaction volumes to ensure it performs reliably under pressure. Use analytics and alerts to monitor operations in real time, giving you visibility and control over your financial activities.
By following these steps, you’ll set up a secure and scalable system tailored to handle high-volume corporate treasury operations effectively.
Related Blog Posts
Ready to modernize your treasury security?
Latest posts
Explore more product news and best practices for using Stablerail.


